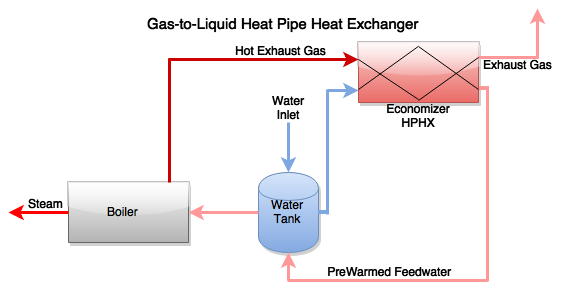
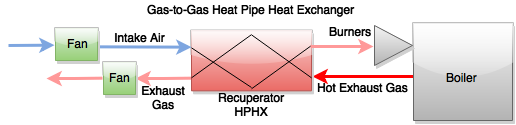
Industrial Waste Heat Recovery (WHR) is the process of recovering heat discharged as a byproduct of one process to provide heat needed by a second process*. So it is the capture and the use of energy contained in fluids or gasses that would otherwise be lost to a facility. In basic terms, waste heat can be interpreted as heat rejected, heat that has already been paid for and is now being rejected from a facility to the environment. This heat still contains a significant amount of energy and usefulness to the facility in terms of transferring heat to another process or as simple as comfort heat to the building space. Recovery and reuse of this heat has the potential for significant reduction of energy costs and improving the profitability and the environmental stewardship of any business. AMSEnergy has taken a systematic approach to defining and implementing waste heat recovery projects for industrial, commercial, and institutional facilities where these opportunities exist.
Industrial Waste Heat Recovery Applications
Combustion Air Preheating
Boiler Feedwater Preheating
Furnace Load Preheating
Generating Low or High Pressure Steam
Comfort Space Heating
Absorption / ADsorption Cooling
Process Water Preheating
Drying
Transfer to Liquid or Gaseous Process Streams
Power Generation (Mechanical)
Steam Rankin Cycle
Organic Rankin Cycle (ORC)
Kalina Cycle
Steam Generation for power generation, mechanical power, or process steam
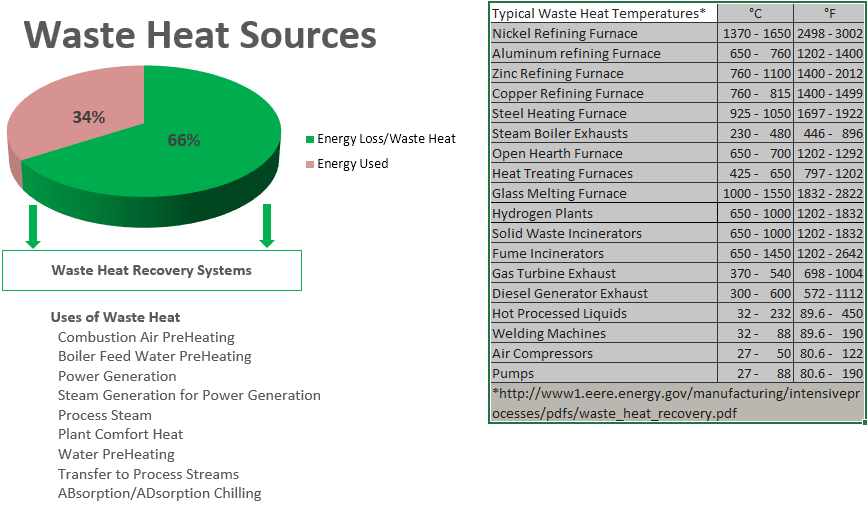
Sources of Industrial Waste Heat
Air Compressors – liquid or air cooled
Boilers
Cooling Towers
Dryers
Furnaces, Ovens, or Kilns
Gas compressor Stations
Flare Gas
Geothermal
Hydraulic Units
Incinerators
Internal Combustion Engines
Engine Jackets
Steam Systems
Thermal Oxidizers
Turbines and Generators
Vacuum Pumps
If it is waste heat, it can be quantified